Amazon USA Sales Analysis
Project Overview
I have worked on analyzing a dataset of over 20,000 sales records from Amazon e-commerce platform. This project involves extensive querying of customer behavior, product performance, and sales trends using PostgreSQL. Through this project, I have tackled various SQL problems, including revenue analysis, customer segmentation, and inventory management.
The project also focuses on data cleaning, handling null values, and solving real-world business problems using structured queries.
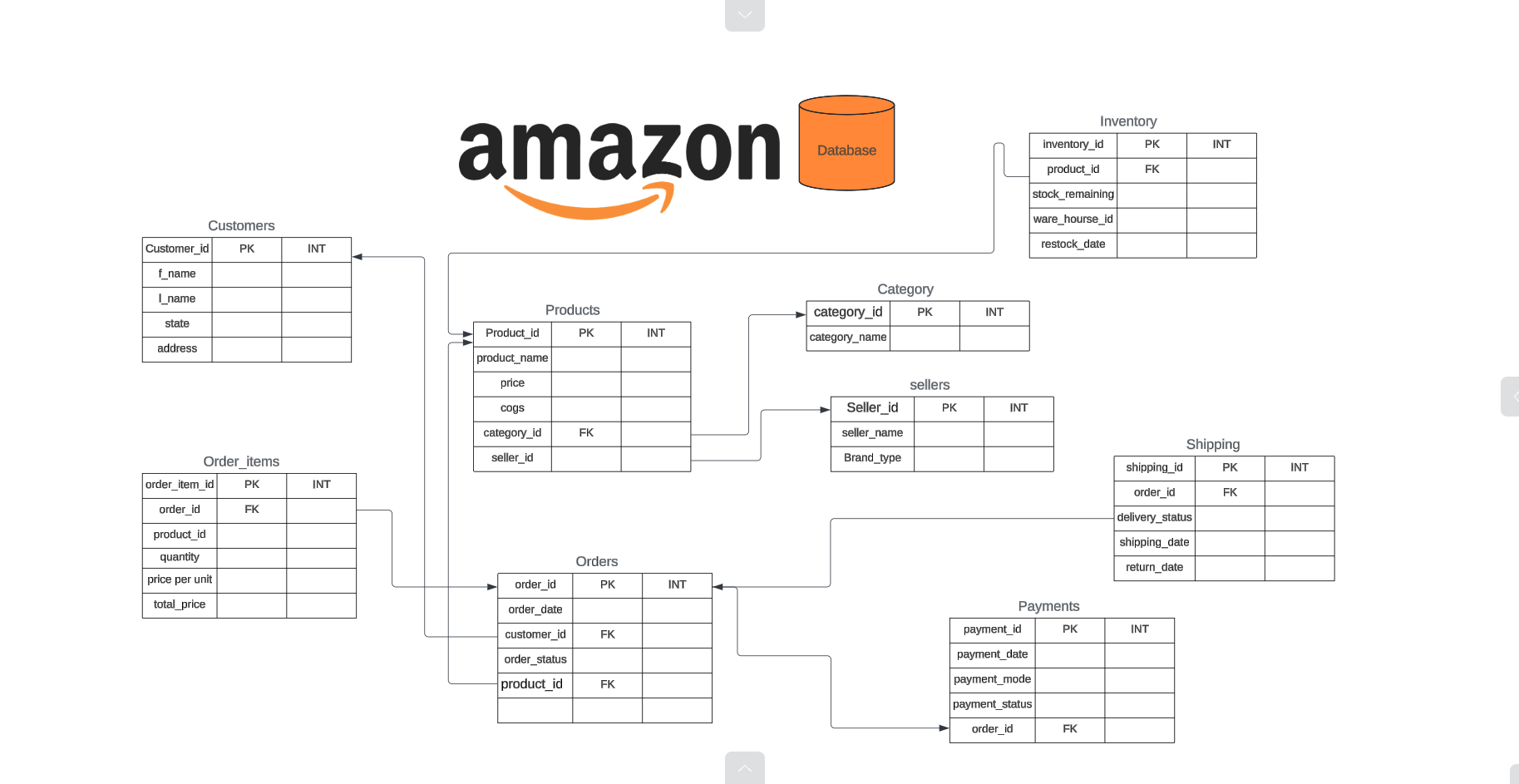
An ERD diagram is included to visually represent the database schema and relationships between tables.
Database Setup & Design
Schema Structure
CREATE TABLE category
(
category_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
category_name VARCHAR(20)
);
-- customers TABLE
CREATE TABLE customers
(
customer_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
first_name VARCHAR(20),
last_name VARCHAR(20),
state VARCHAR(20),
address VARCHAR(5) DEFAULT ('xxxx')
);
-- sellers TABLE
CREATE TABLE sellers
(
seller_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
seller_name VARCHAR(25),
origin VARCHAR(15)
);
-- products table
CREATE TABLE products
(
product_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
product_name VARCHAR(50),
price FLOAT,
cogs FLOAT,
category_id INT, -- FK
CONSTRAINT product_fk_category FOREIGN KEY(category_id) REFERENCES category(category_id)
);
-- orders
CREATE TABLE orders
(
order_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
order_date DATE,
customer_id INT, -- FK
seller_id INT, -- FK
order_status VARCHAR(15),
CONSTRAINT orders_fk_customers FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES customers(customer_id),
CONSTRAINT orders_fk_sellers FOREIGN KEY (seller_id) REFERENCES sellers(seller_id)
);
CREATE TABLE order_items
(
order_item_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
order_id INT, -- FK
product_id INT, -- FK
quantity INT,
price_per_unit FLOAT,
CONSTRAINT order_items_fk_orders FOREIGN KEY (order_id) REFERENCES orders(order_id),
CONSTRAINT order_items_fk_products FOREIGN KEY (product_id) REFERENCES products(product_id)
);
-- payment TABLE
CREATE TABLE payments
(
payment_id
INT PRIMARY KEY,
order_id INT, -- FK
payment_date DATE,
payment_status VARCHAR(20),
CONSTRAINT payments_fk_orders FOREIGN KEY (order_id) REFERENCES orders(order_id)
);
CREATE TABLE shippings
(
shipping_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
order_id INT, -- FK
shipping_date DATE,
return_date DATE,
shipping_providers VARCHAR(15),
delivery_status VARCHAR(15),
CONSTRAINT shippings_fk_orders FOREIGN KEY (order_id) REFERENCES orders(order_id)
);
CREATE TABLE inventory
(
inventory_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
product_id INT, -- FK
stock INT,
warehouse_id INT,
last_stock_date DATE,
CONSTRAINT inventory_fk_products FOREIGN KEY (product_id) REFERENCES products(product_id)
);
Task: Data Cleaning
I cleaned the dataset by:
- Removing duplicates: Duplicates in the customer and order tables were identified and removed.
- Handling missing values: Null values in critical fields (e.g., customer address, payment status) were either filled with default values or handled using appropriate methods.
Handling Null Values
Null values were handled based on their context:
- Customer addresses: Missing addresses were assigned default placeholder values.
- Payment statuses: Orders with null payment statuses were categorized as “Pending.”
- Shipping information: Null return dates were left as is, as not all shipments are returned.
Objective
The primary objective of this project is to showcase SQL proficiency through complex queries that address real-world e-commerce business challenges. The analysis covers various aspects of e-commerce operations, including:
- Customer behavior
- Sales trends
- Inventory management
- Payment and shipping analysis
- Forecasting and product performance
Identifying Business Problems
Key business problems identified:
- Low product availability due to inconsistent restocking.
- High return rates for specific product categories.
- Significant delays in shipments and inconsistencies in delivery times.
- High customer acquisition costs with a low customer retention rate.
Solving Business Problems
Solutions Implemented:
-
Top Selling Products
Query the top 10 products by total sales value.
Challenge: Include product name, total quantity sold, and total sales value.SELECT oi.product_id, p.product_name, SUM(oi.total_sale) AS total_sale, COUNT(o.order_id) AS total_orders FROM orders AS o JOIN order_items AS oi ON oi.order_id = o.order_id JOIN products AS p ON p.product_id = oi.product_id GROUP BY 1, 2 ORDER BY 3 DESC LIMIT 10; -
Revenue by Category
Calculate total revenue generated by each product category.
Challenge: Include the percentage contribution of each category to total revenue.SELECT p.category_id, c.category_name, SUM(oi.total_sale) AS total_sale, SUM(oi.total_sale) * 100.0 / (SELECT SUM(total_sale) FROM order_items) AS contribution FROM order_items AS oi JOIN products AS p ON p.product_id = oi.product_id LEFT JOIN category AS c ON c.category_id = p.category_id GROUP BY 1, 2 ORDER BY 3 DESC; -
Average Order Value (AOV)
Compute the average order value for each customer.
Challenge: Include only customers with more than 5 orders.SELECT c.customer_id, CONCAT(c.first_name, ' ', c.last_name) AS full_name, SUM(total_sale) / COUNT(o.order_id) AS AOV, COUNT(o.order_id) AS total_orders FROM orders AS o JOIN customers AS c ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id JOIN order_items AS oi ON oi.order_id = o.order_id GROUP BY 1, 2 HAVING COUNT(o.order_id) > 5; -
Monthly Sales Trend
Query monthly total sales over the past year.
Challenge: Return current month sale and last month sale.SELECT year, month, total_sale AS current_month_sale, LAG(total_sale, 1) OVER (ORDER BY year, month) AS last_month_sale FROM ( SELECT EXTRACT(YEAR FROM o.order_date) AS year, EXTRACT(MONTH FROM o.order_date) AS month, ROUND(SUM(oi.total_sale::numeric), 2) AS total_sale FROM orders AS o JOIN order_items AS oi ON oi.order_id = o.order_id WHERE o.order_date >= CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL '1 year' GROUP BY 1, 2 ORDER BY year, month ) AS t1; -
Customers with No Purchases
Find customers who registered but never placed an order.
Challenge: List customer details and the time since their registration.Approach 1
SELECT * FROM customers WHERE customer_id NOT IN ( SELECT DISTINCT customer_id FROM orders );Approach 2
SELECT c.* FROM customers AS c LEFT JOIN orders AS o ON o.customer_id = c.customer_id WHERE o.customer_id IS NULL; -
Least-Selling Categories by State
Identify the least-selling product category for each state.
Challenge: Include the total sales for that category within each state.WITH ranking_table AS ( SELECT c.state, cat.category_name, SUM(oi.total_sale) AS total_sale, RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY c.state ORDER BY SUM(oi.total_sale) ASC) AS rnk FROM orders AS o JOIN customers AS c ON o.customer_id = c.customer_id JOIN order_items AS oi ON o.order_id = oi.order_id JOIN products AS p ON oi.product_id = p.product_id JOIN category AS cat ON cat.category_id = p.category_id GROUP BY 1, 2 ) SELECT * FROM ranking_table WHERE rnk = 1; -
Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
Rank customers by CLTV.SELECT c.customer_id, CONCAT(c.first_name, ' ', c.last_name) AS full_name, SUM(total_sale) AS CLTV, DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY SUM(total_sale) DESC) AS cx_ranking FROM orders AS o JOIN customers AS c ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id JOIN order_items AS oi ON oi.order_id = o.order_id GROUP BY 1, 2; -
Inventory Stock Alerts
Products with stock < 10; include last restock and warehouse.SELECT i.inventory_id, p.product_name, i.stock AS current_stock_left, i.last_stock_date, i.warehouse_id FROM inventory AS i JOIN products AS p ON p.product_id = i.product_id WHERE i.stock < 10; -
Shipping Delays
Orders where shipping date is > 3 days after order date.SELECT c.*, o.*, s.shipping_providers, s.shipping_date - o.order_date AS days_took_to_ship FROM orders AS o JOIN customers AS c ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id JOIN shippings AS s ON o.order_id = s.order_id WHERE s.shipping_date - o.order_date > 3; -
Payment Success Rate
Percentage by payment status.SELECT p.payment_status, COUNT(*) AS total_cnt, COUNT(*)::numeric / (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM payments)::numeric * 100 AS pct FROM orders AS o JOIN payments AS p ON o.order_id = p.order_id GROUP BY 1; -
Top Performing Sellers
Top 5 sellers by sales; include success %.WITH top_sellers AS ( SELECT s.seller_id, s.seller_name, SUM(oi.total_sale) AS total_sale FROM orders AS o JOIN sellers AS s ON o.seller_id = s.seller_id JOIN order_items AS oi ON oi.order_id = o.order_id GROUP BY 1, 2 ORDER BY 3 DESC LIMIT 5 ), sellers_reports AS ( SELECT o.seller_id, ts.seller_name, o.order_status, COUNT(*) AS total_orders FROM orders AS o JOIN top_sellers AS ts ON ts.seller_id = o.seller_id WHERE o.order_status NOT IN ('Inprogress', 'Returned') GROUP BY 1, 2, 3 ) SELECT seller_id, seller_name, SUM(CASE WHEN order_status = 'Completed' THEN total_orders ELSE 0 END) AS completed_orders, SUM(CASE WHEN order_status = 'Cancelled' THEN total_orders ELSE 0 END) AS cancelled_orders, SUM(total_orders) AS total_orders, SUM(CASE WHEN order_status = 'Completed' THEN total_orders ELSE 0 END)::numeric / SUM(total_orders)::numeric * 100 AS successful_orders_percentage FROM sellers_reports GROUP BY 1, 2; -
Product Profit Margin
Rank products by profit margin (highest → lowest).SELECT product_id, product_name, profit_margin, DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY profit_margin DESC) AS product_ranking FROM ( SELECT p.product_id, p.product_name, SUM(total_sale - (p.cogs * oi.quantity)) / SUM(total_sale) * 100 AS profit_margin FROM order_items AS oi JOIN products AS p ON oi.product_id = p.product_id GROUP BY 1, 2 ) AS t1; -
Most Returned Products
Top 10 products by return rate.SELECT p.product_id, p.product_name, COUNT(*) AS total_unit_sold, SUM(CASE WHEN o.order_status = 'Returned' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS total_returned, SUM(CASE WHEN o.order_status = 'Returned' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)::numeric / COUNT(*)::numeric * 100 AS return_percentage FROM order_items AS oi JOIN products AS p ON oi.product_id = p.product_id JOIN orders AS o ON o.order_id = oi.order_id GROUP BY 1, 2 ORDER BY 5 DESC LIMIT 10; -
Inactive Sellers
Sellers with no sales in the last 6 months; show last sale date & amount.WITH cte1 AS ( SELECT * FROM sellers WHERE seller_id NOT IN ( SELECT seller_id FROM orders WHERE order_date >= CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL '6 month' ) ) SELECT o.seller_id, MAX(o.order_date) AS last_sale_date, MAX(oi.total_sale) AS last_sale_amount FROM orders AS o JOIN cte1 ON cte1.seller_id = o.seller_id JOIN order_items AS oi ON o.order_id = oi.order_id GROUP BY 1; -
Identify returning vs. new customers
If a customer has > 5 returns → returning; else new.
Challenge: List customer name, total orders, total returns.SELECT c_full_name AS customers, total_orders, total_return, CASE WHEN total_return > 5 THEN 'Returning_customers' ELSE 'New' END AS cx_category FROM ( SELECT CONCAT(c.first_name, ' ', c.last_name) AS c_full_name, COUNT(o.order_id) AS total_orders, SUM(CASE WHEN o.order_status = 'Returned' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS total_return FROM orders AS o JOIN customers AS c ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id JOIN order_items AS oi ON oi.order_id = o.order_id GROUP BY 1 ) AS t; -
Top 5 Customers by Orders in Each State
Include number of orders and total sales per customer.SELECT * FROM ( SELECT c.state, CONCAT(c.first_name, ' ', c.last_name) AS customers, COUNT(o.order_id) AS total_orders, SUM(total_sale) AS total_sale, DENSE_RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY c.state ORDER BY COUNT(o.order_id) DESC) AS rnk FROM orders AS o JOIN order_items AS oi ON oi.order_id = o.order_id JOIN customers AS c ON c.customer_id = o.customer_id GROUP BY 1, 2 ) AS t1 WHERE rnk <= 5; -
Revenue by Shipping Provider
Include orders handled and average delivery time.SELECT s.shipping_providers, COUNT(o.order_id) AS order_handled, SUM(oi.total_sale) AS total_sale, COALESCE(AVG(s.return_date - s.shipping_date), 0) AS average_days FROM orders AS o JOIN order_items AS oi ON oi.order_id = o.order_id JOIN shippings AS s ON s.order_id = o.order_id GROUP BY 1; -
Products with highest YoY revenue decrease (2022 → 2023)
Return product details and decrease ratio.WITH last_year_sale AS ( SELECT p.product_id, p.product_name, SUM(oi.total_sale) AS revenue FROM orders AS o JOIN order_items AS oi ON oi.order_id = o.order_id JOIN products AS p ON p.product_id = oi.product_id WHERE EXTRACT(YEAR FROM o.order_date) = 2022 GROUP BY 1, 2 ), current_year_sale AS ( SELECT p.product_id, p.product_name, SUM(oi.total_sale) AS revenue FROM orders AS o JOIN order_items AS oi ON oi.order_id = o.order_id JOIN products AS p ON p.product_id = oi.product_id WHERE EXTRACT(YEAR FROM o.order_date) = 2023 GROUP BY 1, 2 ) SELECT cs.product_id, ls.revenue AS last_year_revenue, cs.revenue AS current_year_revenue, ls.revenue - cs.revenue AS rev_diff, ROUND((cs.revenue - ls.revenue)::numeric / ls.revenue::numeric * 100, 2) AS revenue_dec_ratio FROM last_year_sale AS ls JOIN current_year_sale AS cs ON ls.product_id = cs.product_id WHERE ls.revenue > cs.revenue ORDER BY 5 DESC LIMIT 10; -
Stored Procedure: record sale & update inventory
Inserts into orders and order_items; decrements inventory.CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE add_sales ( p_order_id INT, p_customer_id INT, p_seller_id INT, p_order_item_id INT, p_product_id INT, p_quantity INT ) LANGUAGE plpgsql AS $$ DECLARE v_count INT; v_price FLOAT; v_product VARCHAR(50); BEGIN SELECT price, product_name INTO v_price, v_product FROM products WHERE product_id = p_product_id; SELECT COUNT(*) INTO v_count FROM inventory WHERE product_id = p_product_id AND stock >= p_quantity; IF v_count > 0 THEN INSERT INTO orders(order_id, order_date, customer_id, seller_id) VALUES (p_order_id, CURRENT_DATE, p_customer_id, p_seller_id); INSERT INTO order_items(order_item_id, order_id, product_id, quantity, price_per_unit, total_sale) VALUES (p_order_item_id, p_order_id, p_product_id, p_quantity, v_price, v_price * p_quantity); UPDATE inventory SET stock = stock - p_quantity WHERE product_id = p_product_id; RAISE NOTICE 'Product % sale added; inventory updated', v_product; ELSE RAISE NOTICE 'Product % is not available', v_product; END IF; END; $$;
Testing Stored Procedure ```sql CALL add_sales (25005, 2, 5, 25004, 1, 14);
Testing Store Procedure call add_sales ( 25005, 2, 5, 25004, 1, 14 );
Learning Outcomes
This project enabled me to:
- Design and implement a normalized database schema.
- Clean and preprocess real-world datasets for analysis.
- Use advanced SQL techniques, including window functions, subqueries, and joins.
- Conduct in-depth business analysis using SQL.
- Optimize query performance and handle large datasets efficiently.
Conclusion
This advanced SQL project successfully demonstrates my ability to solve real-world e-commerce problems using structured queries. From improving customer retention to optimizing inventory and logistics, the project provides valuable insights into operational challenges and solutions.
Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD)